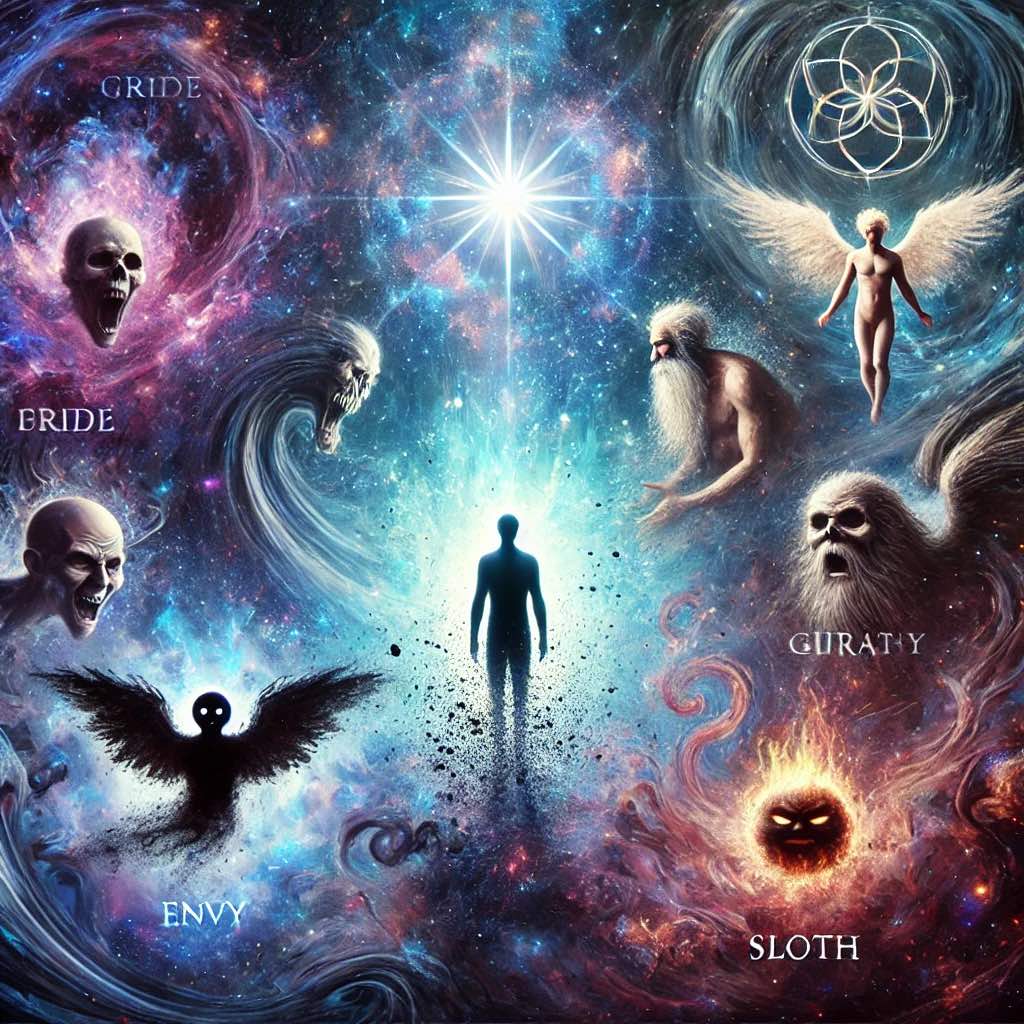
Sins: Why They Matter
To deepen our understanding of sins, it is essential to explore their definitions, their presence across religiTo deepen our understanding of sins, it is essential to explore their definitions, presence across religious texts, and influence on personal development. By detailing specific sins and how they manifest in life, we can better comprehend the spiritual and energetic distortions they cause and the importance of avoiding them. In this approach, we will utilize comparative theology and integrate principles from quantum psychology to illustrate how sins are not merely moral infractions but energetic disturbances that block spiritual growth.
1. What Are Sins? A Comparative Overview
Across different religions, sins are defined as actions, thoughts, or behaviors that go against divine or universal laws. These violations disrupt not only spiritual harmony but also personal well-being, affecting the individual on multiple levels, spiritual, psychological, and even physical. In this expanded view, sins can be seen as obstacles preventing us from living in alignment with our higher selves, creating spiritual and energetic blockages that hinder personal growth and fulfillment.
To understand these more deeply, we explore the nature of sins within various religious traditions:
- Christianity: Sins are viewed as transgressions against God’s will and are categorized as “mortal” (serious sins that sever one’s connection with God) or “venial” (lesser sins that damage but don’t completely sever that connection). This view emphasizes the relationship between actions and spiritual consequences.
- Islam: In Islam, sins are actions that violate Allah’s commands and are divided into “major” (Kabira) and “minor” (Saghira) sins. Major sins require repentance (Tawbah) for forgiveness, emphasizing the importance of spiritual discipline and sincere intention.
- Hinduism: In Hinduism, sins (papa) create negative karma, disrupting one’s dharma (righteous duty) and hindering spiritual liberation (moksha). Sins here are seen as misalignments with the cosmic order and natural law.
- Buddhism: Buddhism does not explicitly use the concept of sin; instead, it focuses on actions rooted in ignorance, attachment, and aversion that generate suffering. Avoiding these actions helps reduce suffering and promotes spiritual progress toward enlightenment.
By comparing these religious traditions, we see that sins are viewed universally as actions that disrupt spiritual and moral harmony. They are energetic misalignments that create blockages, hindering one’s ability to align with higher spiritual truths.
2. The Seven Deadly Sins: A Closer Look
The Christian tradition defines seven primary sins, also known as the “seven deadly sins,” which form the foundation of moral and spiritual teachings. When analyzed through a spiritual and energetic lens, these sins reveal how they distort one’s vibrational state and affect personal and spiritual growth:
- Pride: The belief in one’s superiority, leading to arrogance and a disconnect from humility and gratitude. It creates an energetic barrier that blocks genuine relationships and growth.
- Greed: An excessive desire for material possessions or wealth, which fixates energy on external validation and accumulation rather than inner abundance and fulfillment.
- Lust: Uncontrolled craving for physical or sensual pleasures that objectify others, disconnecting one from authentic emotional and spiritual intimacy.
- Envy: Resentment toward others for their possessions, status, or achievements, leading to dissatisfaction and a lack of contentment, blocking the flow of gratitude and positivity.
- Gluttony: Overindulgence in food or material goods, prioritizing bodily satisfaction over spiritual growth and creating stagnation in the energetic flow.
- Wrath: Uncontrolled anger that manifests as violence or hatred, blocking love and understanding, and resulting in negative energetic imprints.
- Sloth: Laziness or refusal to act, preventing personal and spiritual progress by trapping the individual in inertia and low energy.
These sins, beyond their moral implications, serve as energetic blockages that distort one’s energetic and psychological state, affecting their trajectory in life and spiritual evolution.
3. Quantum Psychology: The Energetic Impact of Sins
Quantum psychology suggests that every action, thought, and intention generates energy. When we commit sins or engage in negative behaviors, we disrupt the energy field around us, blocking the flow of positive, harmonious energy. These distortions create patterns that attract further negativity, reinforcing a cycle of misalignment and suffering.
Examples:
- Pride: A sense of superiority vibrates at a lower frequency, preventing unity and gratitude. This vibration blocks the ability to attract meaningful relationships and fulfillment, keeping one isolated and disconnected.
- Greed: Greed focuses energy on accumulation rather than contribution, which disrupts the natural flow of abundance. The attachment to material gain creates anxiety, fear of loss, and a pervasive sense of lack, despite external successes.
4. The Spiritual and Energetic Consequences of Specific Sins
a. Pride: The Root of All Sins
Pride is considered the root of all sins in many theological traditions because it elevates the self above all else. This false sense of superiority disrupts the flow of humility, gratitude, and divine grace, isolating the individual.
- Impact on Life: Pride creates a lack of empathy, making it difficult to connect with others genuinely. It prevents access to higher states of consciousness, which require humility and surrender.
- Quantum Psychology Perspective: Pride forms an energetic barrier that blocks the flow of love and understanding, trapping one in a low vibrational state that attracts conflict and dissatisfaction.
b. Greed: The Insatiable Desire
Greed, defined as an excessive desire for power or possessions, distances one from spiritual fulfillment. It is condemned in Christianity and Islam, while Hinduism views attachment to material things as an obstacle to liberation.
- Impact on Life: Greed often leads to a cycle of dissatisfaction, where happiness is tied to external gains. This craving can result in unethical actions, strained relationships, and spiritual emptiness.
- Quantum Psychology Perspective: Greed creates an energetic distortion that focuses on taking rather than giving. This disrupts the flow of abundance, creating a mismatch where the individual seeks external validation instead of accessing internal fulfillment.
c. Envy: The Destructive Comparison
Envy, or resenting others for their success, leads to self-destructive thoughts and behavior, distancing one from gratitude and self-worth.
- Impact on Life: Envy clouds one’s ability to appreciate personal blessings, creating a cycle of negativity. In relationships, it breeds resentment and conflict.
- Quantum Psychology Perspective: Envy emits a frequency of scarcity, reinforcing the belief of inadequacy and attracting situations that affirm this belief.
d. Wrath: The Energetic Blockage of Anger
Wrath, or uncontrolled anger, destroys peace and compassion. It affects the physical, mental, and emotional states, leading to stress and isolation.
- Impact on Life: Chronic anger disrupts relationships and impacts health, creating emotional and energetic distance.
- Quantum Psychology Perspective: Anger creates a blockage that traps one in a low frequency, attracting more conflict and preventing spiritual growth.
5. Why Avoiding Sins Is Essential for Personal Development
Avoiding sins is crucial for maintaining alignment with one’s higher self and energy. When one engages in virtuous behaviors—such as humility, generosity, and forgiveness, they elevate their vibrational frequency, attracting positive experiences and fostering personal growth.
The Path to Holistic Growth
Sins are not merely moral transgressions but energetic disturbances that obstruct personal and spiritual development. By understanding their impact through the lenses of comparative theology and quantum psychology, individuals can align their actions with higher values, enabling growth and spiritual fulfillment.







Comments